13.1.1 ALTER DATABASE Syntax
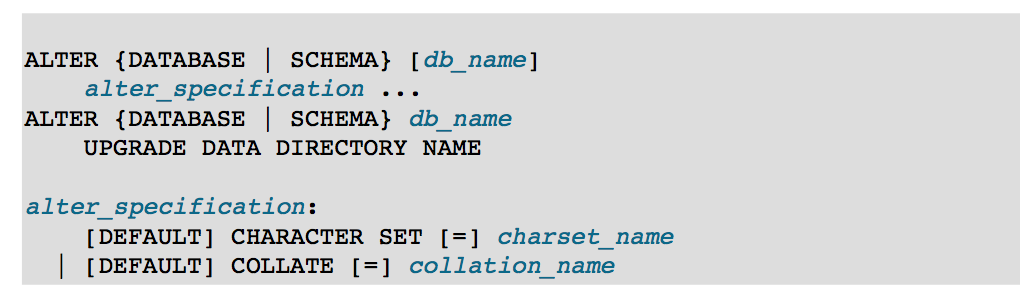 ALTER DATABASE enables you to change the overall characteristics of a database. These characteristics are stored in the db.opt file in the database directory. To use ALTER DATABASE, you need the ALTER privilege on the database. ALTER SCHEMA is a synonym for ALTER DATABASE .
ALTER DATABASE enables you to change the overall characteristics of a database. These characteristics are stored in the db.opt file in the database directory. To use ALTER DATABASE, you need the ALTER privilege on the database. ALTER SCHEMA is a synonym for ALTER DATABASE .
The database name can be omitted from the firs syntax, in which case the statement applies to the default database.
National Language Characteristics
The CHARACTER SET clause changes the default database character set. The COLLATE clause changes the default database collation. Section 10.1 "Character Set Support", discusses character set and collation names.
You can see what character sets and collations are available using, respectively, the SHOW CHARACTER SET and SHOW COLLATION statements. See section 13.7.5.3 "SHOW CHARACTER SET Syntax", and Section 13.7.5.4 "SHOW COLLATION Syntax", for more information.
If you change the default character set or collation for a database, stored routines that use the database defaults must be dropped and recreated so that they use the new defaults(In a stored routine, variables with character data types use the database defaults if the character set or collation are not specified explicitly. See Section 13.1.16, "CREATE PROCDURE and CREATE FUNCTION Syntax".)
Upgrading from Versions Older than MySQL 5.1
The syntax that includes the UPGRADE DATA DIRECTORY NAME clause updates the name of the directory associated with database to use the encoding implemented in MySQL 5.1 for mapping database names to database directory names (See Section 9.2.3, "Mapping of Identifiers to File Names"). This clause is for use under these conditions:
- It is intended when upgrading MySQL to 5.1 or later from older version.
- It is intended to update a database directory name to the current encoding format if the name contains special characters that need encoding.
- The statement is used by mysqlcheck(as invoked by mysql_upgrade)
For example, if a database in MySQL 5.0 has the name a-b-c, the name contains instances of the -(dash) character. In MySQL 5.0, the database directory is also named a-b-c, which is not necessarily safe for all file systems. In MySQL 5.1 and later, the same database name is encoded as a@002db@002dc to produce a file system-neutral directory name.
When a MySQL installation is upgraded to MySQL 5.1 or later from an older version, the server displays a name such as a-b-c(which is in the old format) as #mysql150#a-b-c, and you must refer to the name using the #mysql150# prefix. Use UPGRADE DATA DIRECTORY NAME in this case to explicitly tell the server to re-encode the database directory name to the current encoding format:
ALTER DATABASE `#mysql150#a-b-c` UPGRADE DATA DIRECTORY NAME;
After executing this statement, you can refer to the database as a-b-c without the special #mysql150# prefix.
注
The UPGRADE DATA DIRECTORY NAME clause is deprecated in MySQL 5.7.6 and will be removed in a future version of MySQL. If it is necessary to convert MySQL 5.0 database or table names, a workaround is to upgrade a Mysql 5.0 installation to MySQL 5.1 before upgrading to a more recent release.