Http请求中Content-Type讲解以及在Spring MVC中的应用
引言:在Http请求中,我们每天都在使用Content-type来指定不同格式的请求信息,但是却很少有人去全面了解content-type中允许的值有多少,这里将讲解Content-Type的可用值,以及在SpringMVC中如何使用它们来映射请求信息。
Content-Type
MediaType,即是Internet Media Type, 互联网媒体类型;也叫做MIME类型,在Http协议消息头中,使用Content-Type来表示具体请求中的媒体类型信息。
类型格式:type/subtype(;parameter)?type
主类型:任意的字符串,如text,如果是*号代表所有
subtype 子类型,任意的字符串,如果html,如果是*号代表所有
parameter 可选,一些参数,如Accept请求头的q参数,Content-Type的charset参数
例如:Content-Type:text/html;charset:utf-8;
常见的媒体格式类型如下:
- text/html: HTML格式
- text/plain: 纯文本格式
- text/xml: XML格式
- image/gif: gif图片格式
- image/jpeg: jpg图片格式
- image/png: png图片格式
以application开头的媒体格式类型:
- application/xhmtl+xml: XHTML格式
- application/xml: XML数据格式
- application/atom+xml: Atom XML聚合格式
- application/json: JSON数据格式
- application/pdf: pdf格式
- application/msword: Word文档格式
- application/octet-stream: 二进制流数据(如常见的文件下载)
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded: <form encType="" >中默认的encType,form表单数据被编码为key/value格式发送到服务器(表单默认的提交数据的格式)
另外一种常见的媒体格式是上传文件这时使用的:
- multipart/form-data: 需要在表单中进行文件上传时,就需要使用该格式
以上就是我们在日常的开发中,经常会用到的若干content-type的内容格式。
Spring MVC中关于Content-Type类型信息的使用
首先我们来看看RequestMapping中的Class定义:
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Mapping
public @interface RequestMapping {
String[] value() default {};
RequestMethod[] method() default {};
String[] params() default {};
String[] headers() default {};
String[] consumes() default {};
String[] produces() default {};
}
- value: 指定请求的实际地址,比如/action, /info之类。
- method: 指定请求的method类型,GET、POST、PUT、DELETE等。
- consumes: 指定处理请求的提交内容类型(Content-Type),例如application/json, text/html。
- produces: 指定返回的内容类型,仅当request请求头中的(Accept)类型中包含该指定类型才返回。
- params: 指定request中必须包含某些参数值是,才让该方法处理。
- headers: 指定request中必须包含某些指定的header值,才能让该方法处理请求。
使用示例
headers
示例1
@RequestMapping(value = "/test", method = RequestMethod.GET, headers="Referer=http://www.ifeng.com/")
public void testHeaders(@PathVariable String ownerId, @PathVariable String petId) {
// implementation omitted
}
这里的Headers里面可以匹配所有Header里面可以出现的信息,不局限在Referer信息。
示例2
@RequestMapping(value = "/response/ContentType", headers = "Accept=application/json")
public void response2(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
//表示响应的内容区数据的媒体类型为json格式,且编码为utf-8(客户端应该以utf-8解码)
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
//写出响应体内容
String jsonData = "{\"username\":\"zhang\", \"password\":\"123\"}";
response.getWriter().write(jsonData);
}
服务器根据请求头"Accept=application/json"生产json数据
当你有如下Accept头,将遵守如下规则进行应用:
Accept: text/html, application/xml, application/json将按照如下顺序进行produces的匹配①text/html ②application/xml ③application/json
Accept: application/xml;q=0.5,application/json;q=0.9,text/html
将按照如下顺序进行produces的匹配①text/html ②application/json ③application/xml
参数为媒体类型的质量因子,越大则优先权越高(从0到1)Accept: */*, text/*, text/html
将按照如下顺序进行produces的匹配①text/html ②text/* ③*/*
即匹配规则为:最明确的优先匹配。
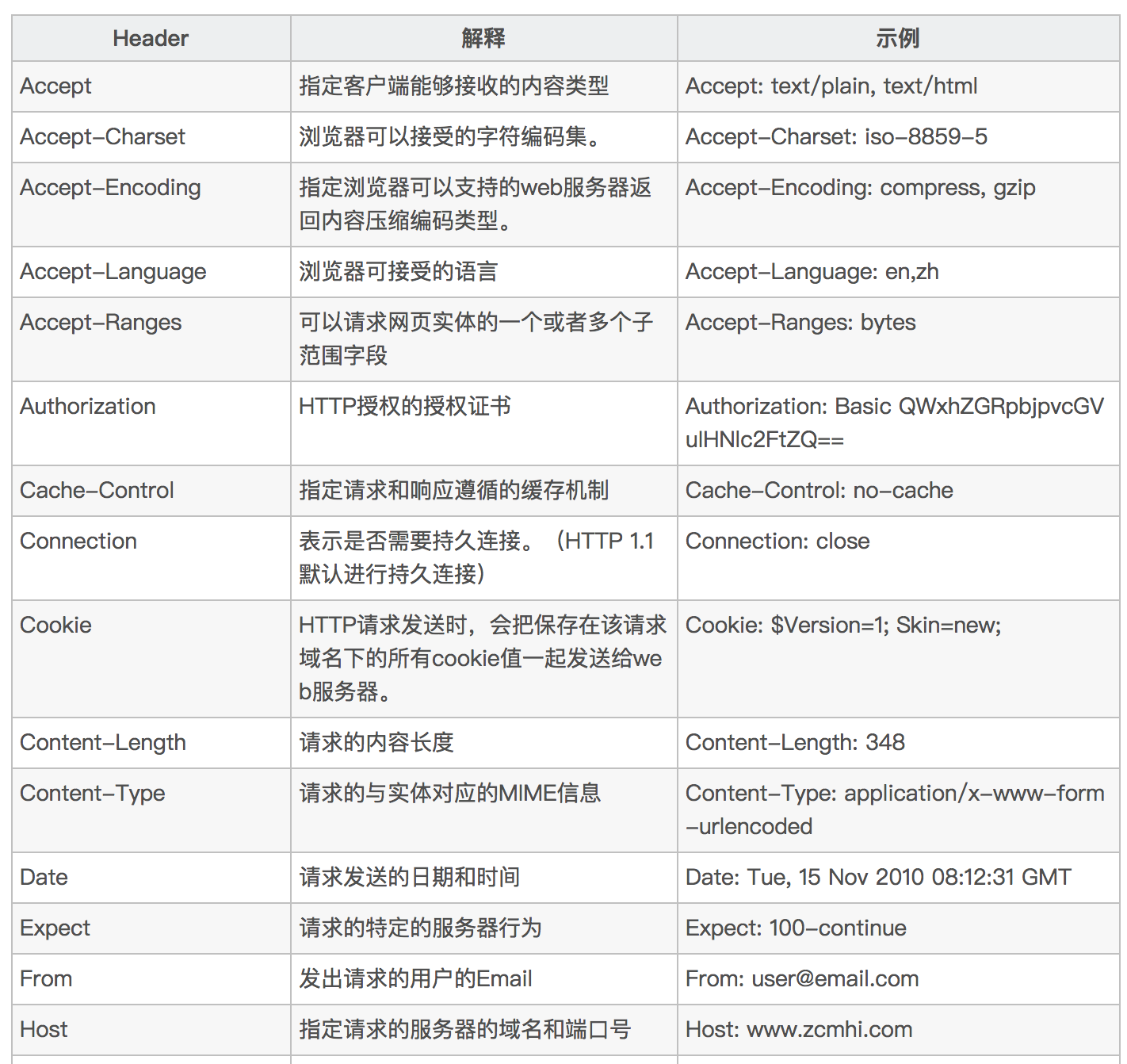
Requests

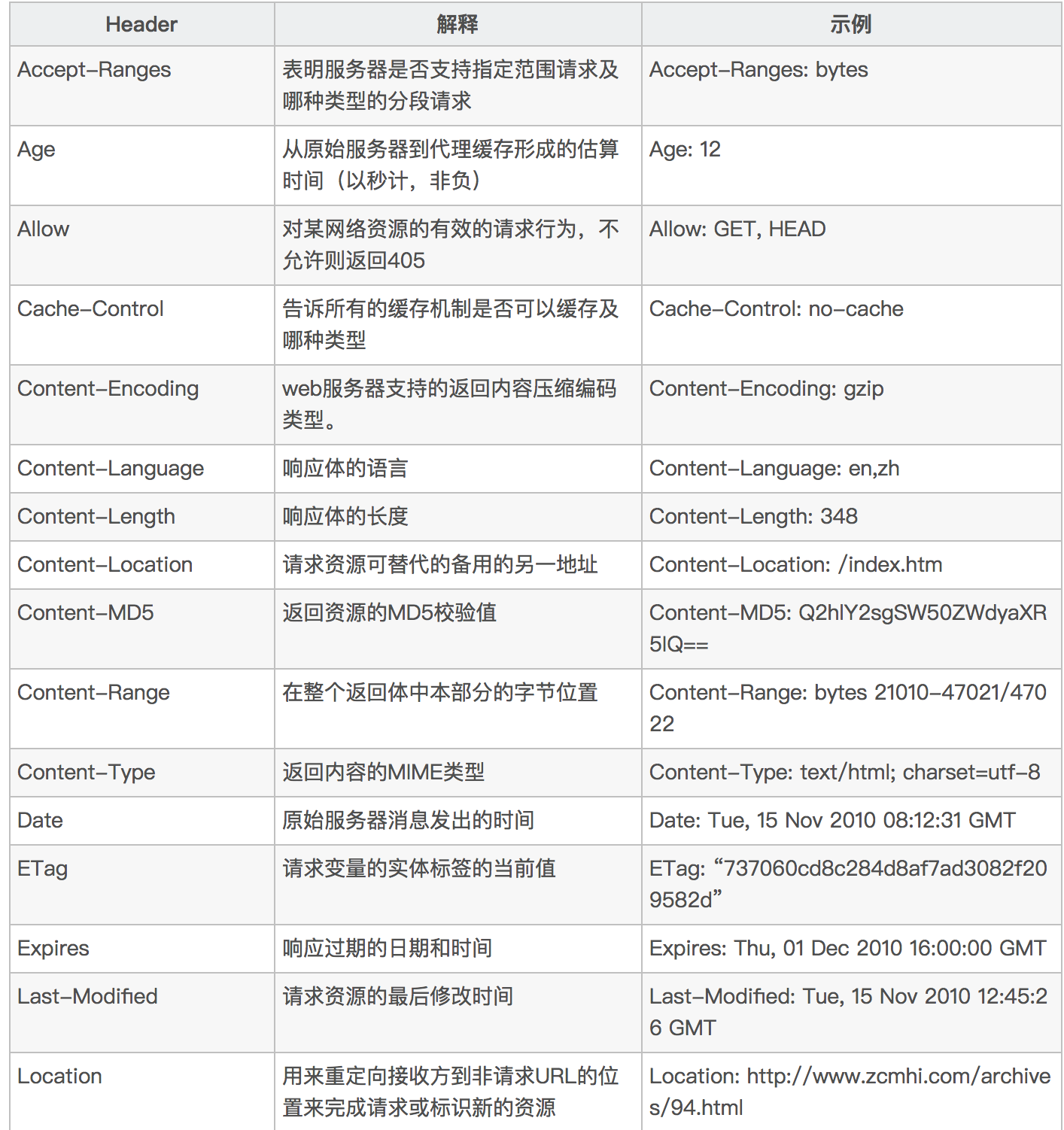
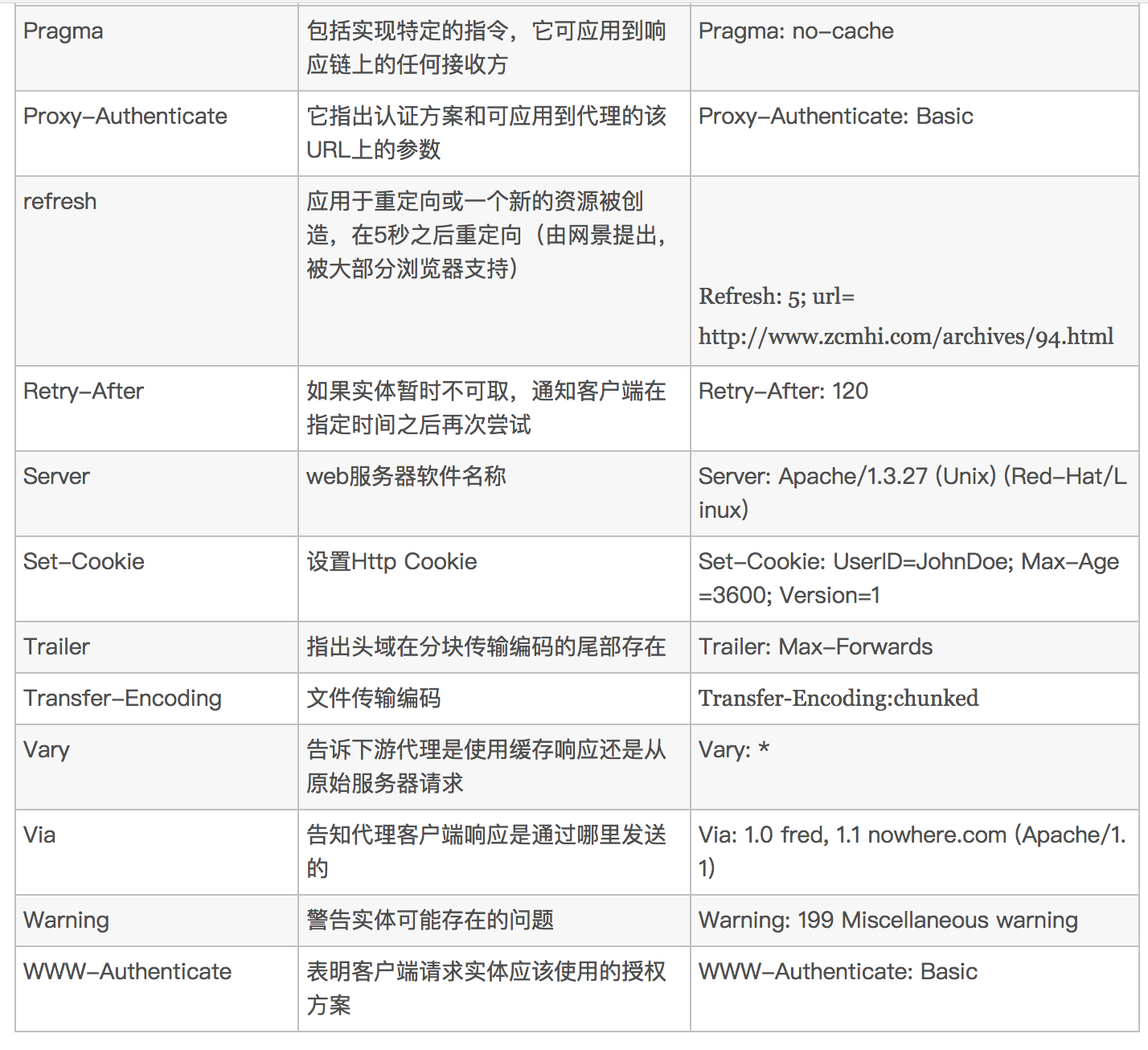
Response部分
params的示例
@RequestMapping(value = "/test/{userId}", method = RequestMethod.GET, params="myParam=myValue")
public void findUser(@PathVariable String userId) {
// implementation omitted
}
仅处理请求中包含了名为"myParam=myValue"的请求,起到了一个过滤的作用。
consumes/produces
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "/users", method = RequestMethod.POST, consumes="application/json", produces="application/json")
@ResponseBody
public List<User> addUser(@RequestBody User userl) {
// implementation omitted
return List<User> users;
}
方法仅处理request Content-Type为"application/json"类型的请求,produces标识处理request请求中Accept头中包含了"application/json"的请求,同时暗示了返回的内容类型为application/json;
总结
在本文中,首先介绍了Content-Type主要支持的格式内容,然后基于@RequestMapping标注的内容介绍了主要的使用方法,其中,headers,consumers,produces,都是使用Content-Type中使用的各种媒体格式内容,可以基于这个格式内容来进行访问的控制和过滤